Die Casting Services
Start A Die Casting Quote



Parts
Lead Time
Specialist
What is
Die Casting?

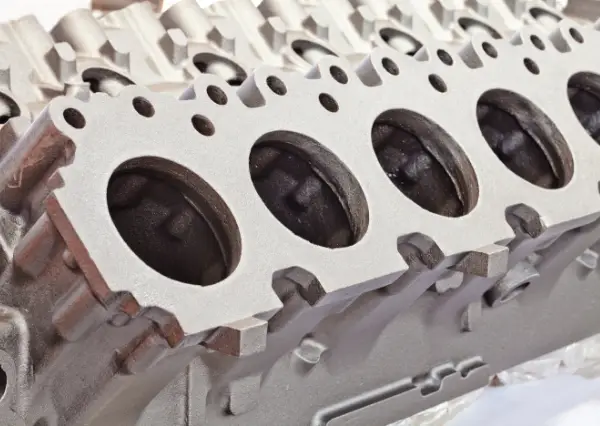
Die casting stands out as a highly efficient process for manufacturing detailed, high-volume metal parts. This process uses specialized molds, known as dies, which are designed to produce multiple parts simultaneously, ensuring efficiency and consistency. Typically used for metals such as aluminum and zinc, die casting involves melting the metal and injecting it under high pressure into these molds.
The rapid cooling and solidification that follows capture the intricate designs and details of the parts, reducing the need for extensive secondary operations. However, some projects may require additional post-machining to meet more stringent tolerances.
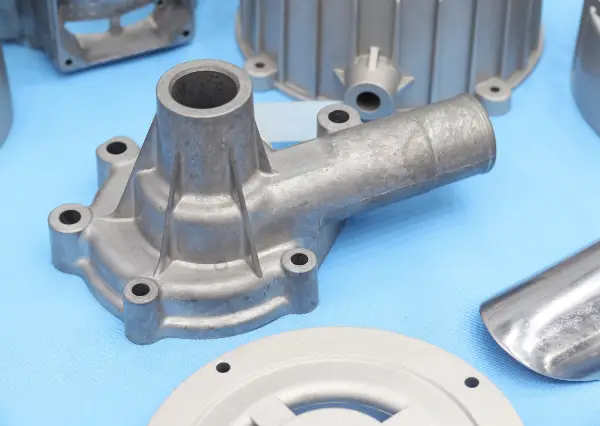
At RapidDirect, our team of experts carefully reviews every die casting project to align our methods with your specific requirements. We prioritize optimizing production flow and ensuring that each part adheres to high standards of durability and aesthetic quality. By focusing on advanced casting techniques and utilizing precision die casting machines, we help you achieve superior results in both functionality and appearance, ultimately enhancing the overall value of your products.
Die Casting Materials

Lightweight and strong, aluminum is ideal for automotive and aerospace parts requiring durability and minimal weight.
- Aluminum ADC12、ADC6、A360、A380

Known for its toughness, zinc enables precise, high-tolerance casting for intricate designs and durable components.
- Zinc Zamak 3, Zamak 5, Zamak 2, ZA8

The lightest structural metal, magnesium offers an excellent stiffness-to-weight ratio, ideal for weight-sensitive applications.
- Magnesium AZ91D, AM60B

Copper is excellent for parts such as heat sinks and electrical connectors because it conducts heat and electricity very effectively.
- Copper ZQA19-2, ZQA19-4, ZQA19-7, ZQA19-10
Die Casting
Surface Finishing
Choose from our various surface finish options to increase corrosion resistance and add vibrant colors to your die cast parts.

RapidDirect Die Casting
Capabilities
RapidDirect provides a clear overview of our capabilities, highlighting essential performance and quality metrics in our detailed tables.
| Description | |
|---|---|
| Minimum Part Weight | 0.017 kg |
| Maximum Part Weight | 12 kg |
| Minimum Part Size | ∅17 mm × 4 mm |
| Maximum Part Size | 300 mm × 650 mm |
| Minimum Wall Thickness | 0.8 mm |
| Maximum Wall Thickness | 12.7 mm |
| Quality Control | ISO 9001 Certified |
| Minimum Possible Batch | 1000 pcs |
for Die Casting





Types of Die Casting Processes

Hot Chamfer Die Casting
It is highly efficient for metals with lower melting points such as zinc and magnesium. This method features a furnace integrated with the casting machine, allowing quick and continuous cycling. The molten metal is injected directly from the heated chamber into the mold, making it ideal for components requiring precise dimensional control and enhanced mechanical properties.

Cold Chamfer Die Casting
It is preferred for metals with higher melting points, including aluminum and copper alloys. The process involves manually loading the molten metal into the cold chamber before each injection, which helps protect the equipment from the intense heat, thereby enhancing its durability and performance. This technique is particularly beneficial for manufacturing large, sturdy parts with complex designs and superior strength.
Applications of Die Casting
Die casting is a versatile manufacturing process used across various industries due to its precision and reliability. Here are some key applications:
- Automotive: Components like engine blocks, gearboxes, and pistons are commonly produced using die casting for their durability and tight tolerances.
- Consumer Electronics: Used in making robust and intricate parts for gadgets such as smartphones, laptops, and cameras.
- Lighting: Creates complex shapes for light fixtures and components, ensuring precision and quality.
- Medical Devices: Produces high-precision instruments and equipment parts, crucial for reliability and sterility in the medical field.
- Industrial Machinery: Parts for heavy machinery that require high strength and resistance to harsh environments.

Advantages of Die Casting
Die casting offers several significant advantages that make it a preferred method for manufacturing metal parts across various industries:
- High Precision and Consistency: Achieves tight tolerances and complex geometries consistently, ideal for mass production of high-quality parts.
- Speed: Fast production cycles due to the high-speed filling and rapid cooling of the molten metal, enabling large volumes of parts to be manufactured quickly.
- Strength and Weight: Produces parts that are durable yet lightweight, thanks to the dense and fine-grained metal structure formed under high pressure.
- Minimal Waste: Efficient material usage with minimal scrap, reducing waste and often decreasing the need for secondary machining.
Disadvantages of Die Casting
Die casting, while beneficial for many applications, has some limitations:
- High Initial Costs: Setting up for die casting can be expensive due to the cost of dies and machinery, making it less economical for small production runs.
- Limited to Certain Metals: Primarily suitable for metals with lower melting points; high-melting metals can be challenging and less efficient to cast.
- Porosity: The rapid cooling of molten metal can lead to air entrapment, resulting in porous parts which may affect structural integrity.
- Size Restrictions: More effective for smaller components; larger parts may present challenges in maintaining dimensional accuracy and uniformity.
- Post-Processing: While minimal, some die casting parts require additional machining or finishing to meet specific tolerances or surface finishes.
FAQs
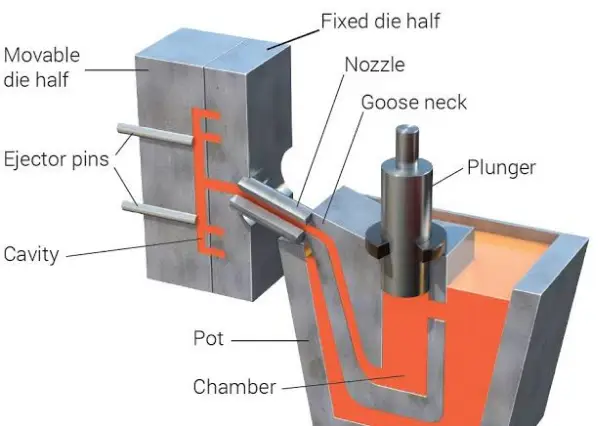
Die casting is a metal casting process characterized by forcing molten metal under high pressure into a mold cavity. The mold, also known as a “die,” is created using two hardened tool steel dies that have been machined into shape and work similarly to an injection mold during the process. Here’s how it works:
- Mold Preparation: The die is prepared and lubricated to facilitate the easy removal of the casting and to aid in controlling the temperature.
- Molten Metal Injection: Molten metal is injected into the die under high pressure, ranging from approximately 10 to 175 megapascals (1,500 to 25,000 psi). The pressure is maintained until the casting solidifies.
- Cooling and Solidification: The molten metal cools quickly in the mold, solidifying into the shape of the desired part.
- Ejection: Once solidified, the die halves are opened, and the cast part is ejected.
- Trimming: Excess material from the casting, such as gates, runners, and flash, is trimmed away.
When designing parts for die casting, several key considerations must be addressed to ensure optimal performance and manufacturability:
- Wall Thickness: Maintain uniform wall thickness to promote even cooling and solidification, reducing risks of defects like warping or internal stresses. Thin walls are preferred for faster cooling and material savings, but their feasibility depends on the metal used and part complexity.
- Draft Angles: Include draft angles in the design to facilitate the easy removal of the casting from the die. Typically, a minimum draft angle of 1 to 2 degrees is necessary, depending on the depth of the part.
- Fillet and Radii: Incorporate fillets and radii to eliminate sharp corners and edges, which can cause stress concentrations and crack initiation points. This adjustment also enhances the flow of molten metal within the die.
- Gating System: Design an efficient gating system to ensure proper flow of the molten metal into the die, minimizing turbulence and air entrapment. The placement of gates influences material distribution and part quality.
- Venting: Proper venting must be planned to allow air and gases to escape from the mold cavity during metal injection. This helps prevent porosity and incomplete filling.
- Simplifying Geometry: Simplify the geometry as much as possible to avoid undercuts and complex features that require intricate die mechanisms, which can increase tooling costs and complicate the casting process.
In die casting, vibrations refer to mechanical oscillations that occur within the die casting machines and molds.
Vacuum Pressure Casting: This process involves creating a vacuum in the mold cavity to minimize air entrapment and porosity. Vibrations in this setting can disrupt the vacuum, leading to defects in the final product.
Low Pressure Casting: Here, metal is introduced into the mold under low pressure, which can be susceptible to vibrations that affect the steady flow of molten metal, impacting the consistency and integrity of the cast.
Semi-Solid Die Casting: Involves injecting semi-solid metal into the mold. Vibrations can influence the thixotropic behavior of the metal, affecting the fill pattern and properties of the final part.
Squeeze Die Casting: This process applies additional pressure after the initial filling to enhance the density and mechanical properties of the cast. Vibrations during this phase can lead to non-uniform pressure application, resulting in inconsistencies.
The lead time for creating die cast tooling usually ranges from 2 to 12 weeks. This time frame starts from the initial design phase, where the concept of the part is developed and its specifications are detailed, to the completion of the mold. The complexity of the part’s design, the specific metal chosen for casting, and the precision required in the final product all significantly influence the duration of the tooling process. Additionally, after the mold is machined, it undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it meets quality standards. Any necessary adjustments or modifications to the mold to correct defects or improve functionality can add to the overall lead time. Effective communication between the manufacturing team and the client is essential to streamline the process and meet production deadlines.
Die casting is a precision manufacturing process that can achieve very tight tolerances, making it ideal for complex, high-volume parts. Generally, the tolerances for die casting depend on the dimensions of the part, the metal used, and the specific casting process. For standard dimensions, tolerances can range from ±0.1 mm for smaller dimensions under 25 mm, to ±0.5 mm for dimensions up to 250 mm. More precise tolerances down to ±0.02 mm can be achieved with additional post-machining processes.
Materials also play a critical role in defining tolerances. Metals like aluminum and zinc alloy have different shrinkage rates and mechanical properties, which influence the final dimensional accuracy. Advanced die casting techniques such as vacuum casting or squeeze casting can further enhance tolerance control by reducing porosity and improving the integrity of the metal.
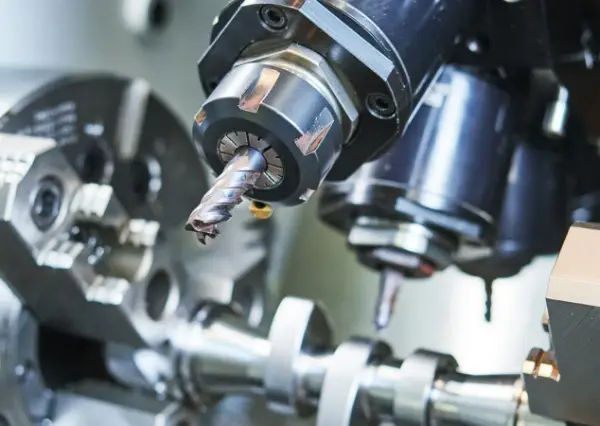
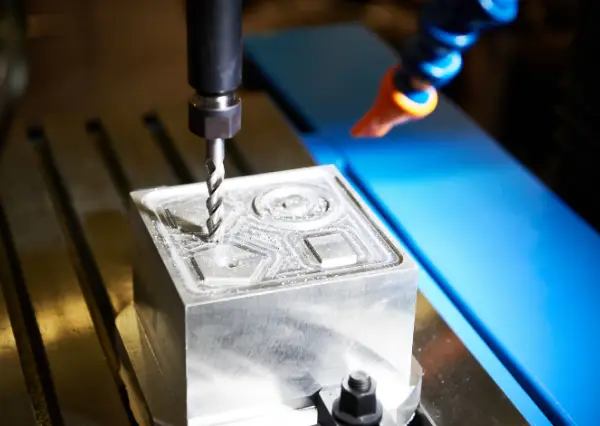
Yes, post-machining of die cast parts is not only possible but often necessary to achieve the desired precision and surface finishes that die casting alone might not provide. Post-machining allows for the attainment of tighter tolerances and smoother surfaces, which are crucial for high-performance and aesthetic requirements. Common post-machining processes include drilling, milling, and CNC machining, which refine the features of the die cast part to exact specifications.
Additionally, post-machining can correct any minor defects that occur during the casting process, such as porosity or surface imperfections. It also enables the addition of complex features and fine details that cannot be achieved through casting alone. By integrating die casting with post-machining, manufacturers can leverage the speed and cost-efficiency of die casting for the rough shape, while achieving the precision of CNC machining for critical dimensions and finishes.
Die Casting
Resources
now, for free